Raspbian VDR Streaming Client - LIRC
Hulk (Diskussion | Beiträge) (Die Seite wurde neu angelegt: „=Lirc - Raspberry Pi mit der Fernbedienung steuern= Der Raspberry Pi bringt bereits am GPIO-Header Anschlussmöglichkeiten für einen IR-Empfänger mit. Mit et…“) |
Version vom 14. Januar 2015, 18:24 Uhr
Lirc - Raspberry Pi mit der Fernbedienung steuern
Der Raspberry Pi bringt bereits am GPIO-Header Anschlussmöglichkeiten für einen IR-Empfänger mit. Mit etwas Bastelgeschick lässt sich ein passender IR-Empfänger für kleines Geld selber bauen. Wie ich das gemacht habe beschreibe ich hier.
Materialliste für den IR-Empfänger
IR-Empfänger: TSOP4836 axial bedrahtet 36 kHz 950 nm oder TSOP4838 axial bedrahtet 38 kHz 950 nm oder TSOP 31236 (Reichelt) Verbindungskabel: RB-CB3-25 Bunt oder RB-CB3-50 Bunt (25cm Länge oder 50cm Länge) Schrumpfschlauch: Dünnwandiger Schrumpfschlauch Ø vor/nach Schrumpfung: 9 mm/3 mm Schrumpfrate 3:1 Schwarz Schrumpfschlauch-Set: Nachfüllbeutel für Schrumpfschlauch-Set 2 : 1 40 mm Bunt 125 St.
Fernbedienung
Da ich noch eine alte TechnoTrend Fernbedienung habe verwende ich vorerst diese. Eine Alternative ist im Bereich Fernbedienungen zu finden. Z.B.
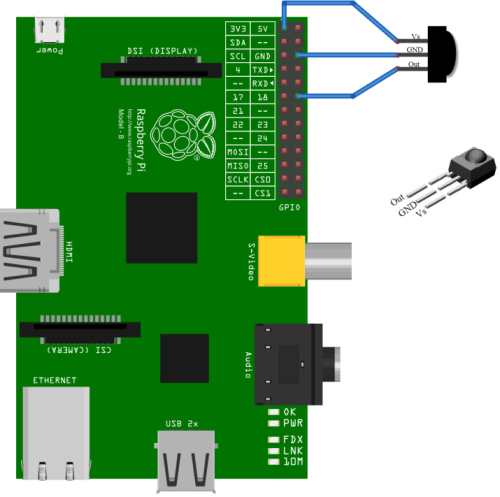
Raspberry Pi Schaltbild
Das gezeigte Schaltbild ist von einem Raspberry Pi Modell B. Die PIN Belegung von einem Raspberry PI B+ ist identisch zu dem Vorgängermodell. Je nach Empfänger muss man die unterschiedlichen Anschlussbelegungen beachten. Immer im Datenblatt nachsehen.
IR-Empfänger zusammenbauen
Ich habe drei Verbindungskabel für meinen IR-Empfänger verwendet (Rot, Schwarz und Lila). Auf einer Seite der Verbindungskabel habe ich die Stecker abgeschnitten und diese, wie auf dem obigen Schaltbild, am TSOP angelötet.
VS: rotes Kabel GND: schwarzes Kabel Out: lila Kabel
Über die einzelnen Lötstellen habe ich Schrumpfschläuche gezogen und diese mit einem Heißluftfön verschmolzen (Feuerzeug geht auch). Wer nicht die einzelnen Verbindungskabel sehen möchte kann nochmals einen Schrumpfschlauch über die gesammten Verbindungskabel ziehen. Zum Schluss werden die Verbindungskabel wie auf dem obigen Schaltbild auf den Raspberry Pi aufgesteckt.
Lirc Konfiguration
Module laden
sudo modprobe lirc_rpi
Module in den Autostart
Damit die Module nach einem System start automatisch geladen werden müssen diese in die modules eingetragen werden.
sudo cp /etc/modules /etc/modules_orig sudo vi /etc/modules
lirc_rpi
Lirc device ermitteln
ls -l /dev/lir*
crw-rw---T 1 root video 247, 0 Jan 4 12:23 /dev/lirc0
Hardware konfiguration
sudo cp /etc/lirc/hardware.conf /etc/lirc/hardware.conf_orig sudo vi /etc/lirc/hardware.conf
# Run "lircd --driver=help" for a list of supported drivers. DRIVER="default" # usually /dev/lirc0 is the correct setting for systems using udev DEVICE="/dev/lirc0" MODULES="lirc_rpi"
Neustarten des Lirc Daemon
sudo /etc/init.d/lirc restart
Erster Test vom IR-Empfänger
Kernelmodul laden
sudo modprobe lirc_rpi
dmesg |grep lirc lirc_dev: IR Remote Control driver registered, major 248 lirc_rpi: module is from the staging directory, the quality is unknown, you have been warned. lirc_rpi: auto-detected active low receiver on GPIO pin 18 lirc_rpi lirc_rpi.0: lirc_dev: driver lirc_rpi registered at minor = 0 lirc_rpi: driver registered!
Hier ist zu sehen das der IR-Empfänger am GPIO Pin 18 erkannt wird.
Prüfen ob Signale der Fernbedienung ankommen
sudo /etc/init.d/lirc stop mode2 -d /dev/lirc0
Danach ein paar Tasten auf der Fernbedienung drücken, wenn alles funktionoiert sollte es so aussehen:
space 3260954 pulse 876 space 805 pulse 1718 space 1636 pulse 1722 space 1630 pulse 1724 space 1632 pulse 1714 space 820 pulse 864 space 795 pulse 882 space 793 pulse 886 space 799 pulse 874 space 1638 pulse 882
Anlernen der Fernbedienung
Datei mit gültigen Lirc Namespaces erstellen
sudo irrecord --list-namespace | grep KEY &> ~/lirc_strings.txt
Aus dieser Datei holt Ihr euch dann die passenden Namen für eure Tasten. Anzeigen der Datei:
sudo cat ~/lirc_strings.txt
Anlernmodus starten
sudo /etc/init.d/lirc stop sudo irrecord -d /dev/lirc0 ~/lircd.conf
Nach starten dem Dialog auf der Konsole folgen.
irrecord - application for recording IR-codes for usage with lirc Copyright (C) 1998,1999 Christoph Bartelmus(lirc@bartelmus.de) This program will record the signals from your remote control and create a config file for lircd. A proper config file for lircd is maybe the most vital part of this package, so you should invest some time to create a working config file. Although I put a good deal of effort in this program it is often not possible to automatically recognize all features of a remote control. Often short-comings of the receiver hardware make it nearly impossible. If you have problems to create a config file READ THE DOCUMENTATION of this package, especially section "Adding new remote controls" for how to get help. If there already is a remote control of the same brand available at http://www.lirc.org/remotes/ you might also want to try using such a remote as a template. The config files already contain all parameters of the protocol used by remotes of a certain brand and knowing these parameters makes the job of this program much easier. There are also template files for the most common protocols available in the remotes/generic/ directory of the source distribution of this package. You can use a template files by providing the path of the file as command line parameter. Please send the finished config files to <lirc@bartelmus.de> so that I can make them available to others. Don't forget to put all information that you can get about the remote control in the header of the file. Press RETURN to continue.
Now start pressing buttons on your remote control. It is very important that you press many different buttons and hold them down for approximately one second. Each button should generate at least one dot but in no case more than ten dots of output. Don't stop pressing buttons until two lines of dots (2x80) have been generated. Press RETURN now to start recording.
................................................................................ Found const length: 107332 Please keep on pressing buttons like described above. ................................................................................ RC-5 remote control found. Found possible header: 876 828 No repeat code found. Signals are biphase encoded. Removed header. Signal length is 13
Now enter the names for the buttons. Please enter the name for the next button (press <ENTER> to finish recording) KEY_POWER Now hold down button "KEY_POWER". Please enter the name for the next button (press <ENTER> to finish recording) KEY_MUTE Now hold down button "KEY_MUTE". Please enter the name for the next button (press <ENTER> to finish recording) ... ... ...
Lirc Konfiguration einspielen
sudo cp /etc/lirc/lircd.conf /etc/lirc/lircd.conf_orig sudo cp ~/lircd.conf /etc/lirc/lircd.conf sudo /etc/init.d/lirc start
Neustart vom System
sudo init 6
Nach einem Neustart vom VDR wird automatisch das Anlernmenü für die Fernbedienung gestartet.
Optional: VDR und Lirc Konfigurationen
Die beiden untigen Konfigurationen werden durch den Anlernprozess von VDR und Lirc erstellt. Falls Ihr die gleiche Hardware verwendet könnt Ihr die Konfigurationen verwenden und somit den Anlernprozess umgehen.
remote.conf
Ihr könnt euch die remote.conf mittels VDR über das OSD-Anlernprogramm erstellen. Wenn Ihr euch die remote.conf manuell erstellen möchtet müssen die VDR-LIRC Kommandos mit den Tasten aus der obigen IRTrans Konfigurationsdatei zugeordnet werden. Achtung! Die Namen sind Case Sensitive.
sudo vi /var/lib/vdr/remote.conf
LIRC.Up KEY_UP LIRC.Down KEY_DOWN LIRC.Menu KEY_MENU LIRC.Ok KEY_OK LIRC.Back KEY_BACK LIRC.Left KEY_LEFT LIRC.Right KEY_RIGHT LIRC.Red KEY_RED LIRC.Green KEY_GREEN LIRC.Yellow KEY_YELLOW LIRC.Blue KEY_BLUE LIRC.0 KEY_0 LIRC.1 KEY_1 LIRC.2 KEY_2 LIRC.3 KEY_3 LIRC.4 KEY_4 LIRC.5 KEY_5 LIRC.6 KEY_6 LIRC.7 KEY_7 LIRC.8 KEY_8 LIRC.9 KEY_9 LIRC.Play KEY_PLAY LIRC.Pause KEY_PAUSE LIRC.Stop KEY_STOP LIRC.Record KEY_RECORD LIRC.FastFwd KEY_FASTFORWARD LIRC.FastRew KEY_REWIND LIRC.Power KEY_POWER LIRC.Channel+ KEY_CHANNELUP LIRC.Channel- KEY_CHANNELDOWN LIRC.Volume+ KEY_VOLUMEUP LIRC.Volume- KEY_VOLUMEDOWN LIRC.Mute KEY_MUTE LIRC.Schedule KEY_EPG LIRC.Info KEY_INFO
lircd.conf
sudo vi /etc/lirc/lircd.conf
# Please make this file available to others
# by sending it to <lirc@bartelmus.de>
#
# this config file was automatically generated
# using lirc-0.9.0-pre1(default) on Sun Aug 24 12:08:49 2014
#
# contributed by
#
# brand: /home/pi/lircd.conf
# model no. of remote control:
# devices being controlled by this remote:
#
begin remote
name /home/pi/lircd.conf
bits 13
flags RC5|CONST_LENGTH
eps 30
aeps 100
one 867 810
zero 867 810
plead 884
gap 107337
toggle_bit_mask 0x800
begin codes
KEY_UP 0x154D
KEY_DOWN 0x1551
KEY_MENU 0x1559
KEY_OK 0x154F
KEY_BACK 0x1553
KEY_LEFT 0x154E
KEY_RIGHT 0x1550
KEY_RED 0x1554
KEY_GREEN 0x1555
KEY_YELLOW 0x1556
KEY_BLUE 0x1557
KEY_0 0x154C
KEY_1 0x1543
KEY_2 0x1544
KEY_3 0x1545
KEY_4 0x1546
KEY_5 0x1547
KEY_6 0x1548
KEY_7 0x1549
KEY_8 0x154A
KEY_9 0x154B
KEY_PLAY 0x157B
KEY_PAUSE 0x157E
KEY_STOP 0x157C
KEY_RECORD 0x157A
KEY_FASTFORWARD 0x157F
KEY_REWIND 0x157D
KEY_POWER 0x1541
KEY_CHANNELUP 0x1563
KEY_CHANNELDOWN 0x1564
KEY_VOLUMEUP 0x1565
KEY_VOLUMEDOWN 0x1566
KEY_MUTE 0x1558
KEY_EPG 0x1562
KEY_INFO 0x1552
end codes
end remote